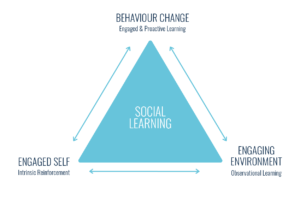
Social learning theory was given by Albert Bandura (1977). Social learning theory is a theory of learning process and social behavior which proposes that new behaviors can be acquired by observing and imitating others. It states that learning is a cognitive process that takes place in a social context and can occur purely through observation of direct instruction, even in the absence of motor reproduction or direct reinforcement.
Adopting the behavior accepted by the society and rejecting the forbidden behavior is the social learning.
Bandura has outlined four measures of social learning attention, retention, reproduction and motivation. Bandura agrees with the behaviorist learning theories of classical conditioning and operant conditioning. However, he adds two important ideas:
- Mediating processes occur between stimuli & responses.
- Behavior is learned from the environment through the process of observational learning and behavior.
Dr. Shobha Kaila
Associate professor
B.Ed. Department
Pestle Weed College of Information Technology



